Another Hashing Power Update!
Bitcoin is once again pushing the boundaries of how much collective computational power its network can reach, briefly pushing past 100,000 PH/s for the first time earlier this week.
At the time of writing, the overall hash rate of the Bitcoin blockchain stands at over 80,000 PH/s, over double what it was one year ago.
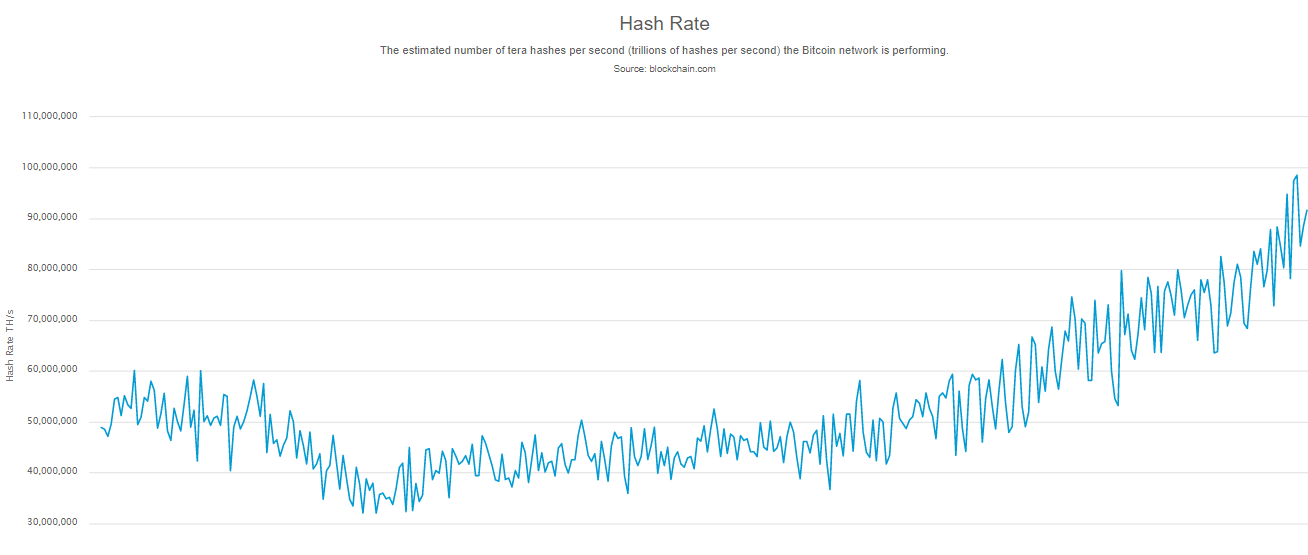
Source: Bitcoin hash rate in the last twelve months, https://www.blockchain.com/charts/hash-rate
It was only a few months ago that we looked at the latest developments with Bitcoin’s hash rate. In the last update, we reported on Bitcoin reaching new all-time highs in the amount of hashing power being pointed at the Bitcoin network by miners, while altcoins running on the Proof-of-Work (PoW) algorithm were suffering from an overall decline, notably in BCH and ETH.

Source: https://www.coinwarz.com/network-hashrate-charts/bitcoin-network-hashrate-chart
Cryptocurrency Mining Has Evolved, With Bitcoin Remaining Firmly on Top
Hash rate is a term used to measure the speed of the machines working on solving and obtaining an alphanumeric piece of data using the PoW algorithm, and not all cryptocurrencies are mineable.
The greater the hashes a machine can generate, the greater chance it has of guessing that critical number and enabling the miner to make profit and generating the next block on the chain. It’s calculated as follows:
1 KH/s is 1,000 (one thousand) hashes per second.
1 MH/s is 1,000,000 (one million) hashes per second.
1 GH/s is 1,000,000,000 (one billion) hashes per second.
1 TH/s is 1,000,000,000,000 (one trillion) hashes per second.
1 PH/s is 1,000,000,000,000,000 (one quadrillion) hashes per second.
1 EH/s is 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 (one quintillion) hashes per second.
1 ZH/s is 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 (one sextillion) hashes per second.
Bitcoin’s hash rate stood at 30,000 PH/s one year ago, and it is often criticized for being centralized due to the dominance over the Bitcoin mining industry that Chinese miners wield.
In the last two years, the distribution of hash rate dominance individual miners possess has spread out amongst the ecosystem. During the Bitcoin crash of 2018, more people began to mine the cryptocurrency, likely because of the reduction in cost and competition with other miners.
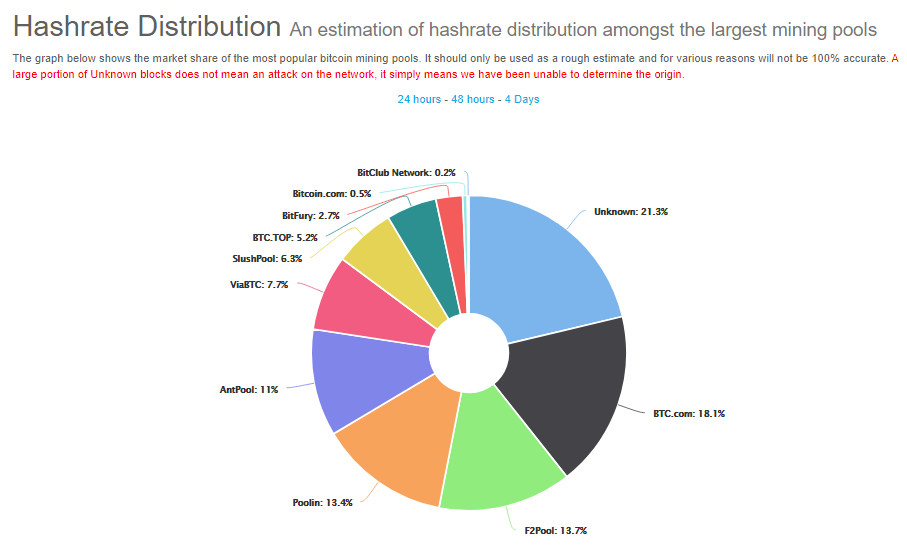
Source: https://www.blockchain.com/pools
If a miner has more than half of the network hashing power, the risk of a 51% attack can occur. This involves bad actors freezing transactions on the network, double-spending, reorganizational attacks, and more.
This has happened to numerous cryptocurrencies, such as Verge, Bitcoin Gold, and even Ethereum Classic, which had a severe double-spend attack. The Bitcoin Cash civil war also posed similar problems for the BCH and BSV networks, with attempts to launch re-org attacks on each other.
Hash rates are often a symbol of how secure a blockchain is and they reflect how much investment is going into the respective cryptocurrency’s ecosystem via mining costs. This is why Bitcoin reaching new hash rate highs is such popular news…
It’s Litecoin’s Turn for its Hash Rate to Decline!
If you compare this report to our previous hashing power updates, in contrary to ETH and BCH, Litecoin’s hash rate often performs stronger than other rival cryptocurrencies using the PoW algorithm, with a strong rise in its hash rate occurring throughout this year.

Source: https://bitinfocharts.com/comparison/hashrate-eth-ltc.html#1y
In mid-July, Litecoin peaked above 500 TH/s, and it currently sits above 300 TH/s. This decline sets back the hash rate by several months and DOESN’T mean Litecoin is in direct trouble, but LTC enthusiasts should keep watch and monitor the situation carefully.
LTC has often been one of the more secure blockchains in the sector. We will keep you updated towards the end of the year on the network stability and hash rate of leading PoW coins.
This is not investment advice; please always do thorough research and only invest what you are willing to lose, especially in times of uncertainty.

